Skeletal System
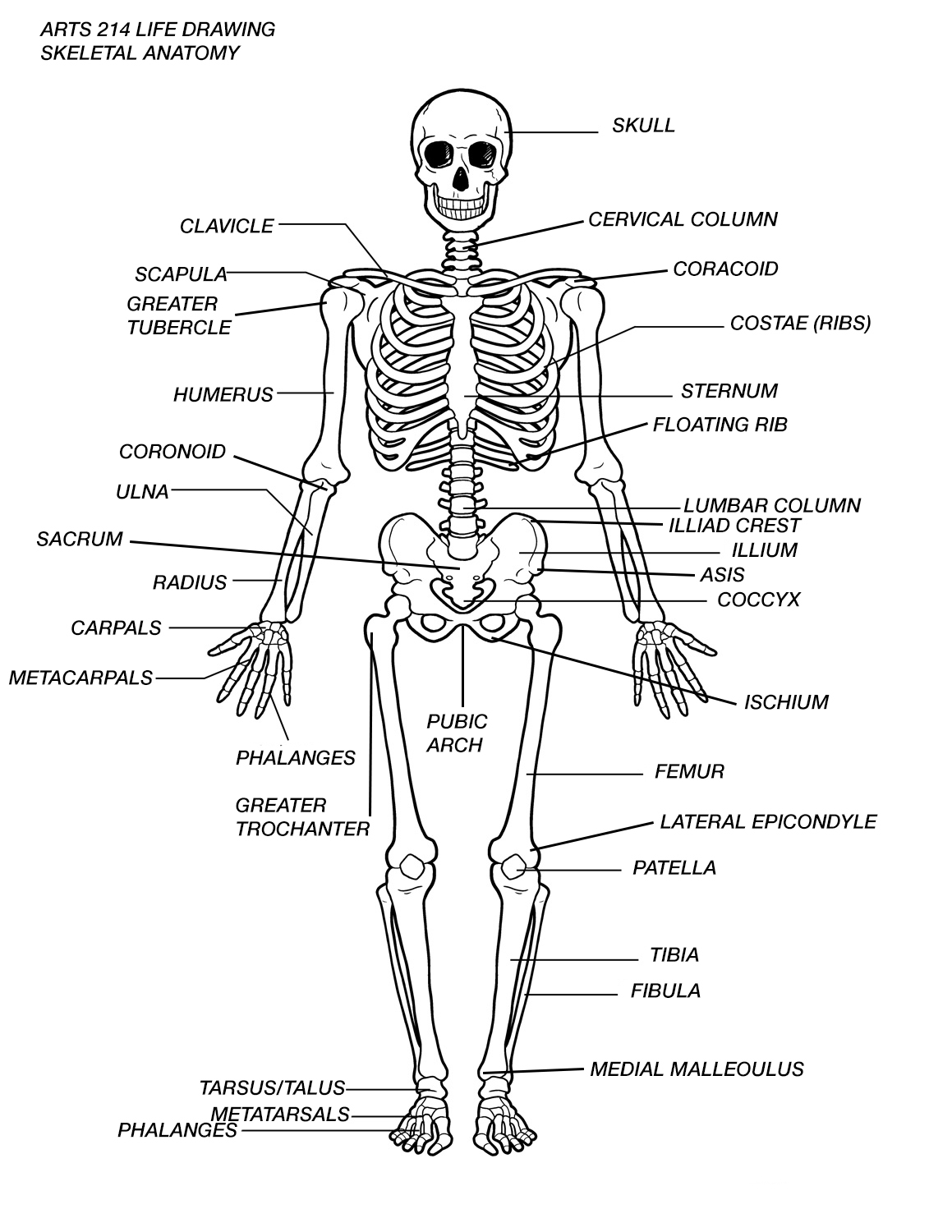 |
| Skeletal system The Skeletal system in an adult body is made up of 206 individual bones. These bones are arranged into two major divisions : the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton.. The axial skeleton runs along the body's midline axis and is made up of 80 bones in the following regions: Skull Hyoid Auditory ossicles Ribs Sternum Vertebral column The appendicular skeleton is made up of 126 bones in the following regions: Upper limbs lower limbs Pelvic girdle pectoral[ shoulder] girdle . Skull The skull is composed of 22 bones those are fused together except for the mandible . These 21 fused bones are separate in children to allow the skull and brain to grow, but fuse to give added strength and protection as an adult . The mandible remains as a movable jaw bone and forms the only movable joint in the skull with the temporal bone . The bones of the superior portion of the skull are known as the cranium and protect the brain from damage . The bones of the inferior and anterior portion of the skull are known as facial bones and support the eyes, nose, and mouth . Hyoid and Auditory Ossicles. The hyoid is a small , U-shaped bone found just inferior to the mandible .The hyoid is the only bone in the body that does not form a joint with any other bone -it is a floating bone.The hyoid's function is to help hold the trachea open and to form a bony connection for the tongue muscles . The malleus, incus, and stapes -known collectively as the auditory ossicles - the smallest bones in the body .Found in a small cavity inside of the temporal bone, they serve to transmit and amplify sound from the eardrum to the inner ear. Vertebrae Twenty -six vertebrae form the vertebral column of the human body. They are named by region : Cervical{neck}-7 vertebrae Thoracic{chest} _12 vertebrae Lumbar {lower back}-5 vertebrae Sacrum-1 vertebra Coccyx {tailbone}-1 vertebra with the exception of the singular sacrum and coccyx , each vertebra is named for the first letter of its region and its position along the superior - inferior axis . For example , the most superior thoracic vertebra is called T1 and the most inferior is called T12. Ribs and Sternum The sternum, or breastbone ,is a thin, knife -shaped bone located along the midline of the anterior side of the thoracic region of skeleton .The sternum connects to the ribs by thin bands of cartilage called the costal cartilage . There are 12 pairs of ribs that together with the sternum form the ribcage of the thoracic region .The first seven ribsare known as ''true ribs'' because they connect the thoracic vertebrae directly to the sternum through their own band of costal cartilage . Ribs 8,9 and 10 all connect to the sternum through cartilage that is connected to the cartilage of the seventh rib ,so we consider these to be ''false ribs. Ribs 11 and 12 are also false ribs , but are also considered to be ''floating ribs'' because they do not have any cartilage attachment to the sternum at all . Pectoral Girdle and Upper Limb The pectoral girdle connects the upper limb[arm] bones to the axial skeleton and consists of the left and right clavicles and left and right scapulae. The humerus is the bone of the upper arm.It forms the ball and socket joint of the shoulder with the scapula and forms the elbow joint with the lower arm bones .The radius and ulna are the two bones of the forearm .The ulna is on the medial side of the forearm and forms a hinge joint with the humerus at the elbow . The radius allows the forearm and hand to turn over at the wrist joint . The lower arm bones form the wrist joint with the carpals, a group of eight small bones that give added flexibility to the wrist . The carpals are connected to the five metacarpals that form the bones of the hand and connect to each of the fingers . Each finger has three bones known as phalanges , except for the thumb , which only has two phalanges. Pelvic Girdle and lower limb Formed by the left and right hip bones , the pelvic girdle connects the lower limb{leg} bones to the axial skeleton. The femur is the largest bone in the body and the only bone of thigh { femoral} region . The femur forms the ball and socket hip joint with the hip bone and the forms the knee joint with the tibia and patella. Commonly called the kneecap , the patella is special because it is one of the few bones those are not present at birth . The patella forms in early childhood to support the knee for walking and crawling . The tibia and fibula are the bones of the lower leg . The tibia is much larger than the fibula and bears almost all of the boy's weight . The fibula is mainly a muscle attachment point and is used to help maintain balance . The tibia and fibula form the ankle joint with the talus , one of the seven tarsal bones in the foot . The tarsals are a group of seven small bones that form the posterior end of the foot and heel . The tarsals form joints with the five long metatarsals of the foot . The each of the metatarsals forms a joint with one of the set of phalanges , except for the big toe, which only has two phalanges . Microscopic Structure of Bones The skeleton makes up about 30-40% of an adult's body mass .The skeleton's mass is made up of nonliving bone matrix and many tiny bone cells . Roughly half of the bone matrix's mass is water , while the other half is collagen protein and solid crystals of calcium carbonate and calcium phosphate . Living bone cells are found on the edges of bones and in small cavities in side of the bone matrix . even though these cells make up very little of the total bone mass , they have several very important roles in the functions of the skeletal system. The bone cells allow bones to grow and develop Be repaired following an injury or daily wear Be broken down to release their stored minerals. Types of bones All of the bones of the body can be broken down into five types : long , short ,flat , irregular , and sesamoid . Long = long bones are longer than they are wide and are the major bones of the limbs . Long bones grow more than the other classes of bone throughout childhood and so are responsible for the hulk of our height as adults. A hollow medullary cavity is found in the center of long bones and serves as a storage area for bone marrow . Examples of long bones include the femur, tibia , fibula , metatarsals , and phalanges . Short . Short bones are about as long as they are wide and often cubed or round in shape . The carpal bones of the wrist and the tarsal bones of the foot are examples of short bones . Flat . Flat bones vary greatly in size and shape ,but have the common feature of being very thin in one direction . Because they are thin , flat bones do not have a medullary cavity like the long bones. The frontal, parietal, and occipital bones of the cranium - along with the ribs and the hip bones - are all examples of flat bones Irregular . Irregular bones have a shape that does not fit the pattern of the long , short , or flat bones , The vertebrae sacrum , and coccyx of the spine- as well as the sphenoid , ethmoid , and zygomatic bones of the skull - are all irregular bones . Sesamoid . The sesamoid bones are formed after birth inside of tenbons that run across joints . Sesamoid bones grow to protect the tenbons from stresses and strains at the joint and can help to give a mechanical advantage to muscles pulling on the tenbons . The patella and the pisiform bone of the carpals are the only sesamoid bones that are counted as part of the 206 bones of the body . Other sesamoid bones can form in the joints of the hands , feet,but are not present in all people . Parts of Bones The long bones of the body contain many distinct region due to the way in which they develop . At birth , each long bone is made of three individual bones separated by hyaline cartilage . Each end bone is called an epiphysis { epi=on;physis=to grow } while the middle bone is called diaphysis {dia=passing through }. The epiphyses and diaphysis grow towards one another and eventually fuse into one bone . The region of growth and eventual fusion in between the epiphysis and disphysis is called the metaphysis {meta= after} . Once the long bone parts have fused together , the on;y hyaline cartilage left in the bone is found as articular cartilage on the ends of the bone that form joints with other bones . The articular cartilage surface acts as a shock absorber and gliding surface between the bones to facilitate movement at the joint . Looking at a bone in cross section, there are several distinct layered regions that make up a one .The outside of a bone is covered in a thin layer of dense irregular connective tissue called the periosteum . The periosteum contains many strong collagen fibers that are used to firmly anchor tenbons and muscles to the bone for movement . Stem cells and osteoblast cells in the periosteum are involved in the growth and the repair of the outside of the bone due to stress and injury . Blood vessels present in the periosteum provide energy to the cells inside of the bone . The periosteum also contains nervous tissue and many nerve endings to give bone its sensitivity to pain when injured . Deep to the compact bone layer is a region of spongy bone where the bone tissue grows in thin columns called trabeculae with spaces foe red bone marrow in between . The trabedulae grow in a specific pattern to resist outside stresses with the lest amount of mass possible , keeping bones light but strong . Long bones have a spongy bone on their ends but have a hollow medullary cavity in the middle m of the diaphysis . The medullary cavity contains red bone marrow during childhood , eventually turning into yellow bone marrow after puberty . Articulation An articulation , joint , is a point of contact between bones , between a bone and cartilage ,or between a bone and a tooth . Synovial joints are the most common type of articulation and feature a small gap between the bones . This gap allows a free range of motion and space for synovial fluid to lubricate the joint . Fibrous joints exist where bones are very tightly joined and offer little to no movement between the bones . Fibrous joints also hold teeth in their bony sockets . Finally cartilaginous joints are formed where bone meets cartilage or where there is a layer of cartilage between two bones . these joints provide a small amount of flexibility in the joint due to the gel-like consistency of cartilage . |



No comments:
Post a Comment